Relevant document types
for logistics
Logistics processes generate a large number of different documents every day – from transport documents and delivery notes to official customs documents. Each of these documents contains structured information about goods, shipments, recipients, senders, or legal requirements that are essential for downstream processes such as billing, customs declarations, or reporting.
In order for goods movements to be handled correctly and processed automatically, it is important to first recognize these documents and place them in the right context. Below you will find an overview of typical logistics documents that occur particularly frequently in daily practice and form the basis of many automated workflows.

Waybills and CMR documents
What is it? The consignment note documents the transport of goods and serves as a contract between the sender and the carrier. For cross-border transport, the CMR consignment note is used—a standardized European document.
Important data:
- Name and address of sender and recipient
- Type and quantity of goods transported
- Transport route and means of transport used
- Special transport instructions or restrictions
Underlying processes: Truck drivers must be informed about what cargo is being transported, where it is going, and what needs to be taken into account. At the same time, the document serves as proof for customs, tax, and liability issues.
Advantages of automation
✅ Digital archiving instead of mountains of paper
✅ Automatic forwarding of relevant information
✅ Interface between paper and digital processes
✅ Immediate availability for all parties involved

Delivery notes and weighing slips
What is it? The consignment note documents the transport of goods and serves as a contract between the sender and the carrier. For cross-border transport, the CMR consignment note is used—a standardized European document.
Important data:
- Name and address of sender and recipient
- Type and quantity of goods transported
- Transport route and means of transport used
- Special transport instructions or restrictions
Underlying processes: Truck drivers must be informed about what cargo is being transported, where it is going, and what needs to be taken into account. At the same time, the document serves as proof for customs, tax, and liability issues.
Advantages of automation
✅Digital archiving instead of mountains of paper
✅ Automatic forwarding of relevant information
✅ Interface between paper and digital processes
✅ Immediate availability for all parties involved

Transport orders
What is it? The transport order is the internal instruction to logistics to transport certain goods from A to B. It contains all the information necessary for execution.
Important data:
- Pickup and delivery address
- Transport dates
- Load details and weight
- Special handling instructions
- Contact details of the contact persons
Underlying processes: Coordination between warehouse, transport, and recipient. Basis for route planning and vehicle dispatching.
Advantages of automation:
✅ Automatic route optimization
✅ Real-time information for all parties involved
✅ Reduced coordination effort

Ocean bills of lading
What is it? The most important document in international maritime trade. It serves as a contract of carriage, proof of receipt, and proof of ownership for the goods being transported.
Important data:
- Shipper and consignee
- Description of goods
- Number of containers or packages
- Port of shipment and port of destination
- Ship information
Underlying processes: Customs clearance, documentation for insurance, basis for payments in international trade.
Advantages of automation
✅ Accelerated customs clearance
✅ Automatic notifications of status changes
✅ Integration into supply chain management

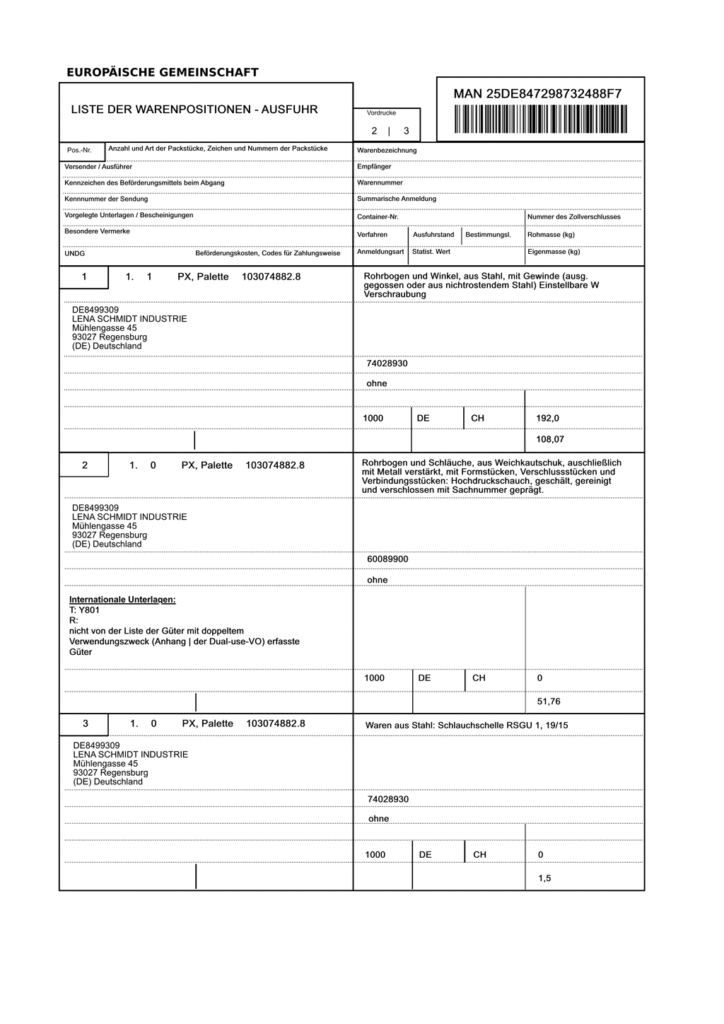
EU export lists and customs documents
What is it? Official documents for cross-border goods traffic within and outside the EU. They document which goods are leaving the country.
Important data:
- Description of goods and customs tariff numbers
- Value and weight of goods
- Country of origin and destination
- Exporter and recipient
Underlying processes: Customs clearance, statistical recording of foreign trade, basis for VAT exemptions.
Advantages of automation
✅ Automatic plausibility checks
✅ Direct transmission to customs authorities
✅ Reduced error rate for complex customs tariff numbers
The common denominator:
time savings and error reduction
All these documents have one thing in common: they contain structured data that can be processed perfectly automatically. The advantages are obvious:
- Time savings:
Documents are processed “live” instead of being typed up manually for hours. - Fewer errors:
People only check instead of re-entering everything. Careless mistakes are a thing of the past. - Better availability:
Digital documents are immediately available to everyone involved. - Traceability:
Automatic archiving creates complete documentation.
The logistics industry is at a turning point: those who still work manually today will lose touch tomorrow. The technology is there—it’s just a matter of using it correctly.
Automated document processing
with AI
The five document types shown have one thing in common: their data structure is ideal for automated processing. And that’s exactly where ExB comes in – with ready-to-use AI models specifically designed for logistics.
Want to see how it works in practice?
👉 Request a demo or learn more about ExB’s AI platform.




